Essential oils have been used for centuries for their aromatic and therapeutic properties. These concentrated plant extracts possess remarkable abilities to influence our mood, emotions, and overall wellbeing. Let's look at the science behind how essential oils affect us, specifically focusing on their impact on the brain and their widespread benefits throughout the body. Prepare to be amazed by the intricate mechanisms at play!
The Olfactory System: Gateway to the Brain
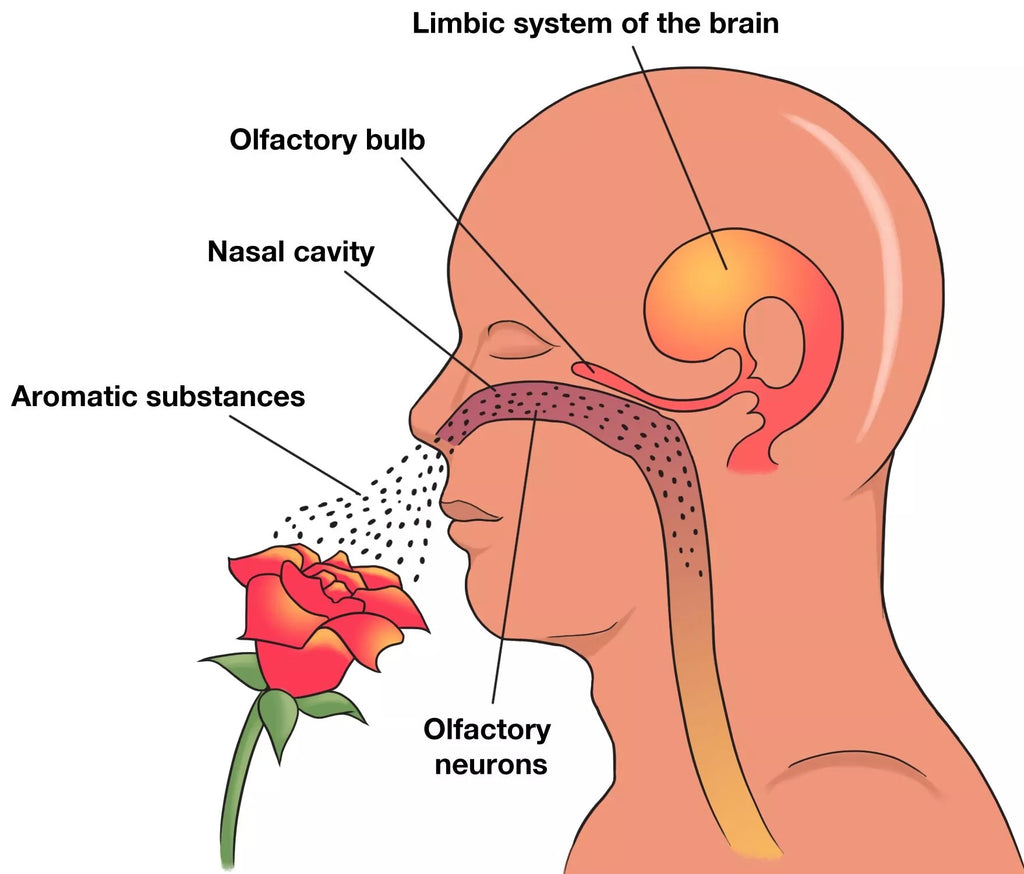
Our olfactory system, responsible for our sense of smell, plays a pivotal role in the interaction between essential oils and our brain. When we inhale the aroma of an essential oil, the molecules in the oil travel through our nasal passages and bind to specialised receptors in our olfactory epithelium. These receptors send signals to the olfactory bulb, which is part of the brain's limbic system, often referred to as the "emotional brain."
Once the signals reach the limbic system, they interact with various regions, including the amygdala and hippocampus, which are responsible for processing emotions and forming memories, respectively. This interaction between the odourant molecules and the limbic system can evoke powerful emotional responses and trigger memories associated with specific scents.
Additionally, the olfactory signals also reach the frontal cortex, the area of the brain responsible for higher cognitive functions such as attention, decision-making, and problem-solving. This explains why certain essential oils can enhance focus, mental clarity, and overall cognitive performance.
Interestingly, the olfactory bulb has direct connections to the limbic system, which is closely associated with emotions, memory, and behaviour. This direct link between the olfactory system and the limbic system is what gives essential oils their profound ability to influence our emotions and mood.
The Limbic System: Emotions and Memory
The limbic system is intimately involved in regulating our emotions, mood, memory, and even certain physiological responses. When essential oil molecules interact with the olfactory bulb, they stimulate the limbic system, triggering a cascade of reactions. This activation can evoke powerful emotional responses, influence our cognitive function, and even enhance memory formation and recall.
Understanding the intricate relationship between essential oils and the limbic system allows us to utilise these natural aromatic compounds to their fullest potential. Whether it's creating a calming atmosphere, promoting relaxation, or boosting focus and concentration, essential oils offer a holistic approach to supporting our emotional and cognitive health.
Neurotransmitters and Neurochemicals
Within the limbic system, essential oils can modulate the production and release of various neurotransmitters and neurochemicals.
One neurotransmitter influenced by essential oils is serotonin. Serotonin is often referred to as the "feel-good" neurotransmitter because it contributes to feelings of relaxation, happiness, and overall wellbeing. Research has shown that inhaling lavender essential oil can increase the release of serotonin in the brain, creating a calming and soothing effect. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing stress, anxiety, or difficulty with sleep.
Another neurotransmitter affected by essential oils is dopamine. Dopamine is associated with feelings of pleasure, motivation, and reward. Citrus oils like bergamot have been found to stimulate the release of dopamine in the brain, promoting a sense of happiness, motivation, and uplifted mood. This can be especially useful for individuals seeking a natural mood booster or those looking to enhance their motivation and productivity.
In addition to serotonin and dopamine, essential oils can also influence the production and release of other neurochemicals within the limbic system. For example, certain oils like frankincense have been found to increase the production of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter known for its calming and relaxing effects. This can help reduce anxiety, improve sleep quality, and promote a sense of tranquility.
Moreover, essential oils can interact with the endorphin system, which is responsible for regulating pain perception and promoting feelings of pleasure and wellbeing. When inhaled or applied topically, essential oils can trigger the release of endorphins, leading to a natural analgesic effect and an overall sense of comfort and relaxation.
The ability of essential oils to influence neurotransmitters and neurochemicals underscores their potential in supporting emotional balance, stress reduction, and overall mental wellbeing. By targeting specific neurotransmitter systems, essential oils can help regulate mood, enhance relaxation, and improve overall emotional state.
It's important to note that the effects of essential oils on neurotransmitters and neurochemicals may vary depending on the individual and the specific oil used. Each essential oil has its own unique chemical composition, which contributes to its specific effects on the brain and body.
The Blood-Brain Barrier and Systemic Effects
As essential oil molecules are inhaled, they not only impact the brain but also enter the bloodstream through the lungs.
The blood-brain barrier serves as a protective mechanism for the brain, shielding it from potentially harmful substances while allowing essential nutrients and certain molecules to pass through. When it comes to essential oils, their small molecular size and lipid solubility enable them to cross this barrier and access the brain.
Once essential oil molecules enter the bloodstream, they can be carried to different parts of the body, including organs, tissues, and cells. This systemic distribution allows for the wide-ranging benefits of essential oils beyond their effects on the brain. For example, when applied topically or inhaled, essential oils can interact with receptors on the skin, respiratory system, and other tissues, influencing various physiological processes.
In addition to their direct effects on organs and tissues, essential oils can also have indirect systemic effects. The aroma of essential oils can stimulate the olfactory receptors in the nose, triggering the activation of the hypothalamus, which is a crucial control center for regulating hormone production and other physiological functions. This can lead to cascading effects on the endocrine system, immune system, and other interconnected systems in the body.
Furthermore, essential oils contain bioactive compounds that can have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. These properties can support the body's natural defenses, promote cellular health, and contribute to overall wellbeing.
It's important to note that the systemic effects of essential oils can vary depending on factors such as the specific oil used, its concentration, the method of application, and individual variations. Some essential oils may have specific affinities for certain organs or systems, while others may have more general effects throughout the body.
Benefits for the Mind and Body
The effects of essential oils extend beyond their influence on emotions and cognition. Different oils possess unique properties and can offer a wide range of benefits. For example:
- Calming and Relaxing: Lavender, chamomile, and ylang-ylang oils have been found to promote relaxation, reduce anxiety, and improve sleep quality.
- Energising and Focus-Enhancing: Citrus oils like lemon, orange, and grapefruit are known for their invigorating properties, boosting mood, and increasing mental clarity.
- Immune-Boosting: Tea tree, eucalyptus, and rosemary oils possess antimicrobial and immune-stimulating properties, supporting the body's natural defence mechanisms.
The science behind the effects of essential oils on our brain and body is a fascinating subject. By leveraging the power of scent, these potent plant extracts can positively influence our emotions, cognition, and overall wellbeing. From the olfactory system to the limbic system and beyond, essential oils engage intricate pathways to provide a multitude of benefits. So next time you inhale the captivating aroma of an essential oil, appreciate the remarkable scientific journey it takes and embrace the transformative effects it offers for your mind and body.
(Note: This blog post provides a general overview of the topic and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.)
Keep exploring our blog! Here are just a few fascinating topics for you to learn about:
